Image Generation from Scene Graph
last modified : 01-09-2018
General Information
- Title: Image Generation from Scene Graph
- Authors: Justin Johnson, Agrim Gupta and Li Fei-Fei
- Link: article
- Date of first submission: 4 April 2018
- Implementations:
Brief
Methods exist to generate image from natural language descriptions. These methods can take various forms, one example of such methods would be RNN coupled with GANs. In this article, the authors propose to improve the results obtained on these methods by capturing more information about the image to generate using scene graphs. No insight is given as to how generate the scene graph as an input.
How Does It Work
To solve the problem they propose an end to end network. The network has two main parts, the first one processes the graph to create the features representative of the description of the image. And the second part takes the features and uses them to create the image representing the scene.
This image from the articles shows the whole pipeline:
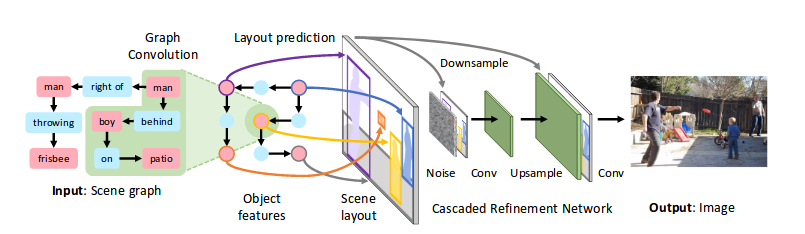
First the input scene graph is transformed while keeping the graph structure. Then boxes and shapes representing the objects of the scene are predicted. Finally, from the representation of the scene, the image is generated with Cascaded Refinement Network. The whole process is trained adversarially using discriminators.
Results
To test the proposed approach, the authors use the mechanical turk. They showed their image as well as the image from the state of the art method and ask the question: "Which image match the caption better ?" (the images were generated using the same caption). They showed that their images were preferred in 67.6\% of the presented pairs of images.
In Depth
Let's describe a bit more each steps of the network.
First the features are generated using the input scene graph. The graph is a series of relation between object, noted as ( , ,), in relation with . All the object are linked to an other one.
From this graph there is a one to one mapping using "graph convolutions" as describe in the following image:
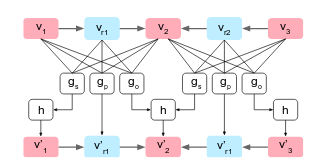
For each vectors describing either a relation or an object , new vectors are output. The function to output the new relation vectors differ from the function used to output the new object vectors because object may be linked to multiple object while relation are only between to objects (usage of the pooling function h).
Then, the new graph of features is processed to go from graph to image:
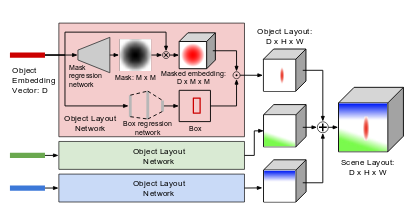
This processing steps is done for each objects and works in two pipelines (inside the red rectangle), the bottom one generates the bounding box of the object to generate, the top one the masked embedding. The masked embedding is then interpolated inside the box in the description matrix. As said before, this step is done for all the objects (blue and green rectangles), and all the generated matrix are merged to get the scene layout.
Finally, the scene layout is presented to a Cascade Refinement Network to generate the final image. For the training they use a pair of discriminator networks and train in a adversarial fashion.